LinkedHashMap实现LRUCache
LinkedHashMap实现原理
简单介绍一下LinkedHasMap的实现原理,针对JDK 8.0,在不同的版本上其实现可能有所区别。
原理概括
LinkedHasMap就是基于HashMap,通过维护一个双向链表,达到在使用HashMap存储的情况下,记录其顺序。
linkedHashMap结构图的示意图如图所示:
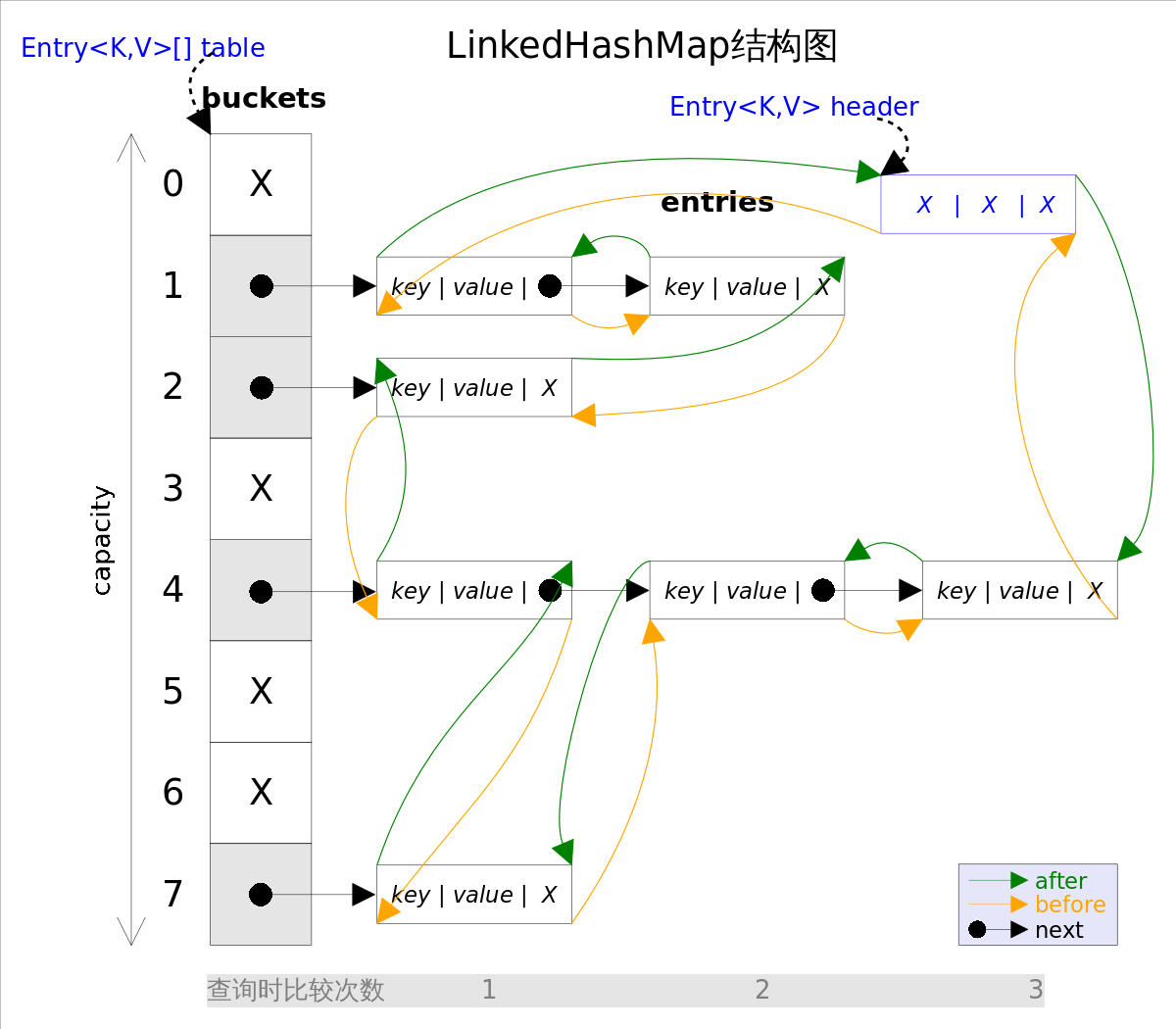
水平所限,本篇不会把所有的实现都呈现出来,只对其其中的几个关键性的方法函数进行解析。
构造方法
其构造方法主要有三个,只介绍其中的一个。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
|
这里的 initialCapacity表示初始的长度,loadFactor表示加载因子,accessOrder表示访问顺序,当其值为true时,表示当前的LinkedHashMap的顺序由访问数据时决定,即数据访问之后就会将这个数据放在LinkedHashMap数据项的前面来,而accessOrder为false时,则表示数据的访问数据由插入时就决定好了。
put方法
往LinkedHashMap里面添加数据的方法就是通过put方法实现,在jdk 8.0中LinkedHashMap并没有自己实现put方法,而是由HashMap一同实现了。下面是具体的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
|
代码略长,长话短说,前面的大部分都是hashMap的实现,到了最后afterNodeInsertion,这个方法就是留给LinkedHashMap去实现其调换顺序的。我们直接看LinkedHashMap中这个方法的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
|
这个方法主要实现在某些情况下,需要将老的数据移除掉,移除就是通过removeNode实现的,我们不往下继续看,只关注其条件。我们观察到 需要移除老数据的添加有三个.
- evict的boolean为true
- head != null
- removeEldestEntry(first) 返回true
其中,evict在调用时就是传入的值true,而head在LinkedHashMap中初始化并添加数据后,就不会为null了,所以这里需要直接移除老数据的关键条件就是removeEldestEntry这个方法了,而这个方法在LinkedHashMap的实现中默认是范围false的,即默认不用移除掉老的数据。那么当我们需要LinkedHashMap存储的数据达到一定量的时候,移除掉老数据就需要重写removeEldestEntry这个方法了。
get
get的实现在LinkedHashMap重写了,实现也很简单,首先判断有没有这个key,如果有,在判断当前的accessOrder是不是为true,如果为true,则需要将顺序按照访问顺序调整一下,然后将数据返回回去。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
|
利用HashMap实现LRUCache
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| class LRUCache {
class Node {
int key;
int value;
Node pre;
Node next;
}
private int capacity;
private Node head, tail;
private Map<Integer, Node> map = null;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>(capacity);
head = new Node();
tail = new Node();
head.pre = null;
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
tail.next = null;
}
public int get(int key) {
Node node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
private void moveToHead(Node node) {
removeNode(node);
addNode(node);
}
private void removeNode(Node node) {
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
private void addNode(Node node) {
node.pre = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.pre = node;
head.next = node;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.key = key;
newNode.value = value;
map.put(key, newNode);
addNode(newNode);
if (map.size() > capacity) {
Node tail = popTail();
map.remove(tail.key);
}
} else {
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
private Node popTail() {
Node node = tail.pre;
removeNode(node);
return node;
}
}
|
